FreeWay
This model is proposed to emulate the motion behavior of mobile nodes on a freeway [3]. The freeway map used in our simulations is shown in Figure 30.
This model can be used in exchanging traffic status or tracking a vehicle on a freeway.
In this model, we use maps. There are several freeways on the map and each freeway has lanes in both directions. The differences between Random Waypoint and Freeway are the following:
a) Each mobile node is restricted to its lane on the freeway.
b) The velocity of mobile node is temporally dependent on its previous velocity.
c) If two mobile nodes on the same freeway lane are within the safety distance (SD), the velocity of the following node cannot exceed the velocity of preceding node.
The inter-node and intra-node relationships involved are: If node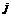 is ahead of node is ahead of node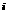 in its lane then: in its lane then:
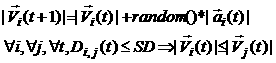
Due to the above relationships, the Freeway mobility pattern is expected to have spatial dependence and high temporal dependence. It also imposes strict geographic restrictions on the node movement by not allowing a node to change its lane.
In our proposed simulation scheme the model has 4 new parameters. This new parameters make our simulation scheme more similar to real world motion of cars in a freeway.
1- Max acceleration which specifies the maximum acceleration that a node can have in a time slot.
2- Fixed acceleration: it is a Boolean parameter that specifies whether a node should have fixed acceleration in each transition or not.
3- Positive speed ratio: if the node can change its acceleration in each transition, its acceleration will be random. Therefore, this parameter specifies the weight of positive acceleration to negative one.
The model’s map also has its special parameters that follow:
1- Points to make the freeway Map,
2- Number of lanes in each direction,
3- Horizontal space between lanes,
4- Horizontal space between lanes in opposite direction
Each point in this model is a handle  . You can add, remove, or move a handle. Note that these handles should be in the map area presented by the size handle. As the sequence of these points are important in constructing the lane, freeway handles have an additional parameter, sequence, which determines the position of handle among others. As you see in Figure 31, you are free to create every map you want. . You can add, remove, or move a handle. Note that these handles should be in the map area presented by the size handle. As the sequence of these points are important in constructing the lane, freeway handles have an additional parameter, sequence, which determines the position of handle among others. As you see in Figure 31, you are free to create every map you want.
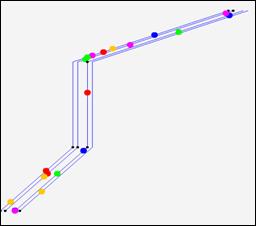
Freeway Mobility Model Map
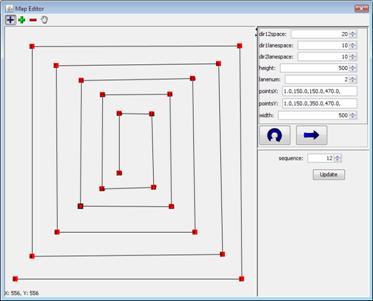
Freeway Model Map Editor window
|